openad-toolkit
Getting Started with OpenAD
- If you haven’t yet done so, install OpenAD first.
- When installing on macOS without a virtual environment, you may need to use
python3andpip3instead ofpythonandpip. - When updating to OpenAD
0.4.0or above, first remove all toolkits by runnninglist toolkitsand thenremove toolkit <toolkit_name>.
Getting Started - CLI
-
Enter the virtual environment
Note: If you just installed OpenAD, you probably already activated the virtual environment.
source ~/ad-venv/bin/activate -
Enter the command shell
openad -
Exit the command shell
Hitctrl+cor run:exit -
Run a single command from outside the command shell
openad <command> -
Exit the virtual environment
deactivate
Running Bash Commands
To run a command in bash mode, prepend it with openad and make sure to escape quotes.
openad show molecules using file \'base_molecules.sdf\'
Getting Started - Jupyter
Setting up Jupyter
The following commands only need to be run once after installation:
-
Activate your virtual environment
Note: If you just installed OpenAD, you probably already activated the virtual environment.
source ~/ad-venv/bin/activate -
Create an iPython kernel
This ports your virtual environment to Jupyter.python -m ipykernel install --user --name=ad-venvNote: To list your installed iPython kernels, you can run
jupyter kernelspec list, and to remove the kernel you can runjupyter kernelspec uninstall ad-venv -
Install the magic commands
This enables OpenAD commands to be run within a Jupyter Notebook.init_magicAlternative: Manually add magic commands
If you don’t want to activate magic commands in all Notebooks, you can instead activate them for individual Notebooks.
- Run
init_examples - Copy the file
~/openad_notebooks/openad.ipynbto the same directory as the Notebook you wish to activate. - In your Notebook, run this inside a code cell:
!run openad.ipynb
- Run
-
Install example Notebooks
This installs our example Notebooks at~/openad_notebooks.init_examples
Launching OpenAD in Jupyter
-
Open any Notebook
The following command will open up the example Notebook:jupyter lab ~/openad_notebooks/Table_of_Contents.ipynb -
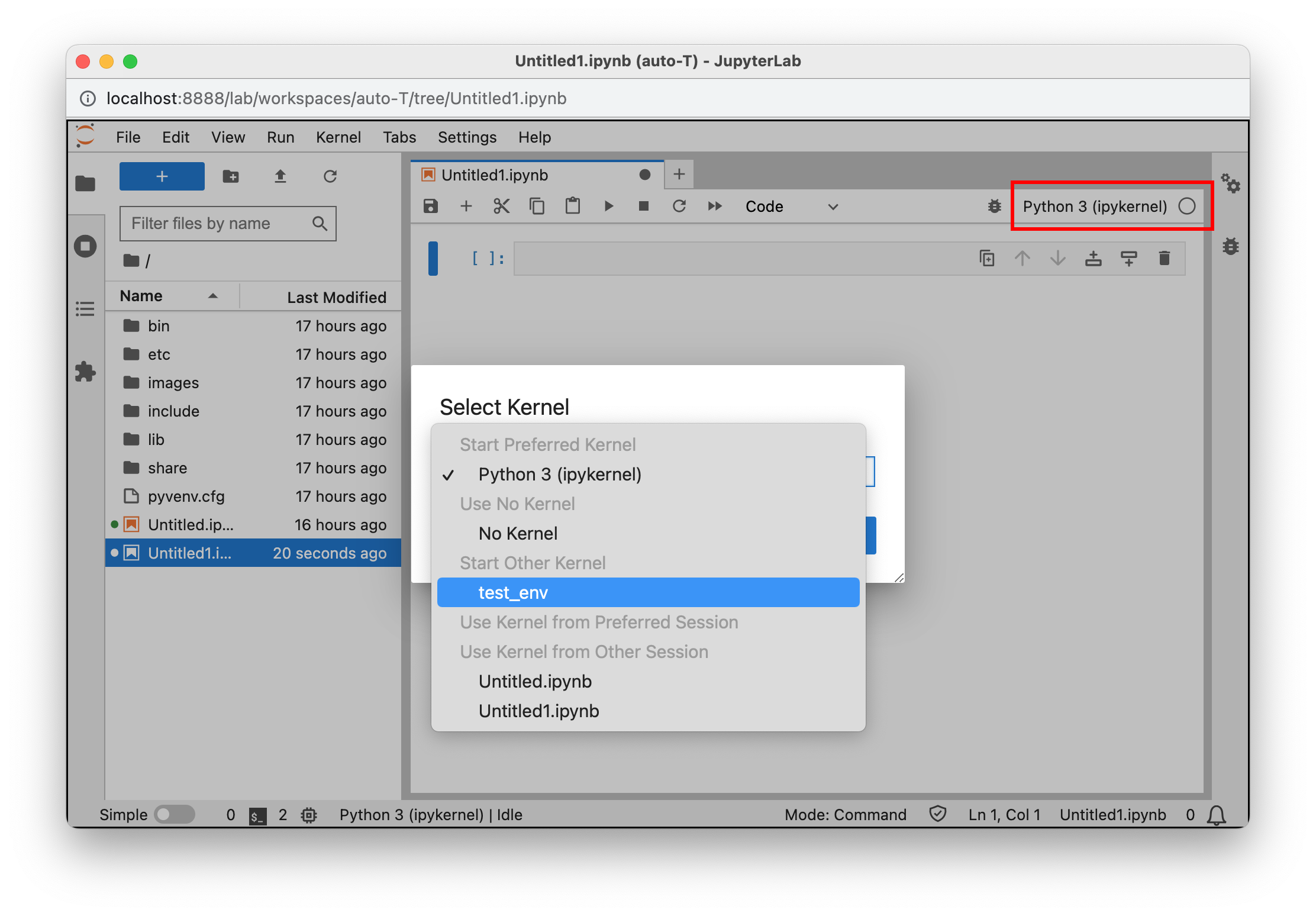
Select the kernel
Make sure to select the “ad-venv” iPython kernel. You can do this under Kernel > Change Kernel, or in the latest versions of Jupyter by clicking the kernel name in the top right hand corner. If you don’t see your iPython kernel, make sure you followed the Jupyter Setup instructions listed above.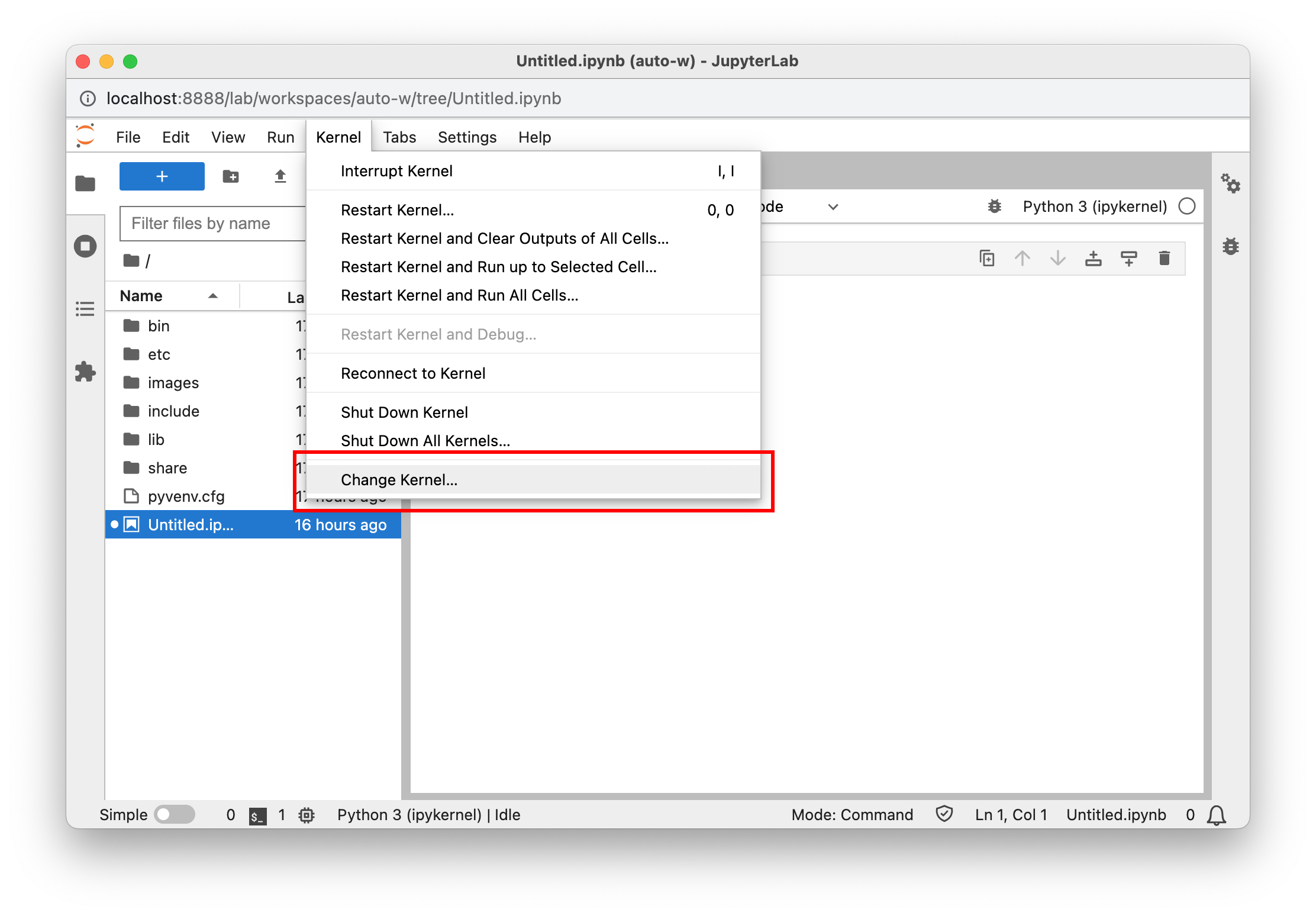
-
Magic Commands
Magic commands let you access any OpenAD CLI command from within Jupyter. They are invoked by the%openadprefix.%openad list filesIf you wish to retrieve data from an OpenAD command, you can use the
%openaddprefix instead. This will return raw, unstyled data for further processing.my_data = %openadd display data 'my_data_file.csv'